|
The potential applications of homomorphic operations over
encryption functions were recognized and appreciated almost
about the same time as the first public-key cryptographic
algorithm RSA was invented. The RSA algorithm is
multiplicatively homomorphic. The ensuing 30 years have
brought on several additively or multiplicatively homomorphic
encryption functions with increasing algorithmic inventiveness
and complicated mathematics. However, it was not clear
until 2009 whether a fully homomorphic encryption algorithm, one
that allows both additive and multiplicative homomorphisms,
would exist. This was resolved by Craig Gentry, and followed
up by several authors who have proposed fully homomorphic
encryption algorithms and addressed issues related to their
formulation, arithmetic,efficiency and security. While
formidable efficiency barriers remain, we now have a
variety of fully homomorphic encryption algorithms that
can be applied to various private computation problems in
healthcare, finance and national security.
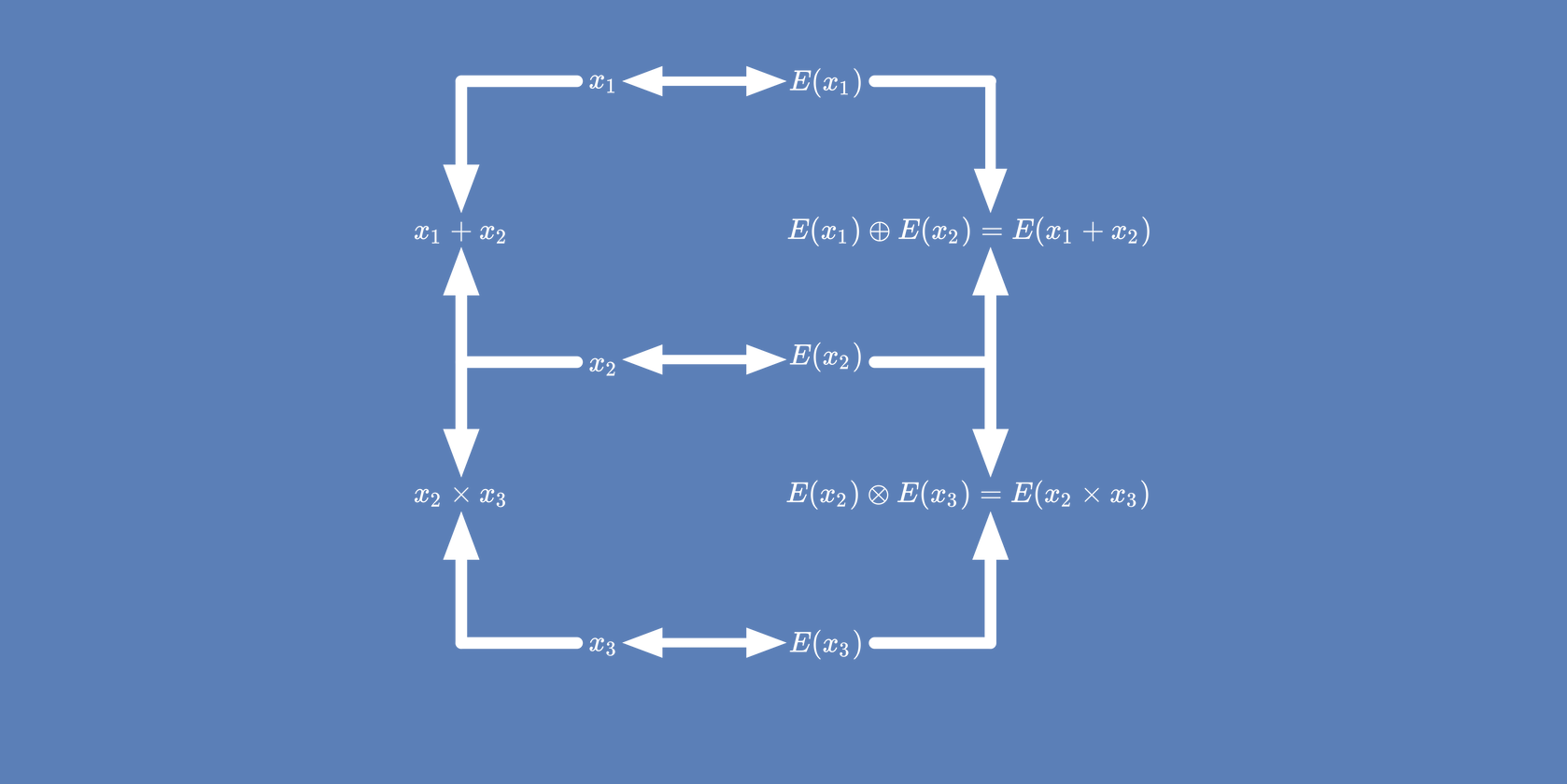
On the other hand partially homomorphic encryption
algorithms allow either additions or multiplications involving
two ciphertexts, but not both. Still, in many cases, additions
and multiplications involving ciphertexts and scalars are
possible, allowing several applications. If a highly efficient
fully homomorphic encryption function for multiple applications
were to become available, the usefulness of partially
homomorphic encryption functions would be in question.
But this lofty end is not yet in sight. Studying partially
homomorphic encryption functions may help us to understand
the difficulties ahead and perhaps to avoid blind alleys and
dead ends. Moreover, partially homomorphic encryption algorithms
may have certain perhaps limited applications for which
significantly more efficient implementations can be obtained.
Selected Publications
- P. He, S. C. Oliva Madrigal, Ç. K. Koç,
T. Bao, and J. Xie.
CASA: A Compact and Scalable Accelerator for Approximate
Homomorphic Encryption. IACR Transactions on
Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems,
Volume 2024, No. 2, to appear, 2024.
pdf
- Ç. K. Koç, F. Özdemir, and Z. Ö. Özger.
Partially Homomorphic Encryption.
Springer, 2021.
URL
→
Machine Learning
|