|
Cryptographic Engineering
Cryptographic engineering
provides techniques, mechanisms, and tools for designing algorithms,
architectures, hardware and software that support private and
authenticated communication, allowing secure and authenticated
transactions over communication networks.
→
continue
|
 |
Finite Field Arithmetic
Finite Field Arithmetic
studies mathematical properties of finite rings and fields in
order to discover novel representations of the elements and
fast algorithms for arithmetic operations for designing efficient
software and hardware for cryptography and error-correcting codes.
→
continue
|
 |
Random Number Generators
Random Number Generators
are used for supplying secret keys, private keys, and ephemeral
and initializing variables in cryptographic systems. Its
foundations are based on cryptographic randomness, in terms of
its entropy under the different measures and its complexity
as methods of representation and underlying mathematical functions.
→
continue
|
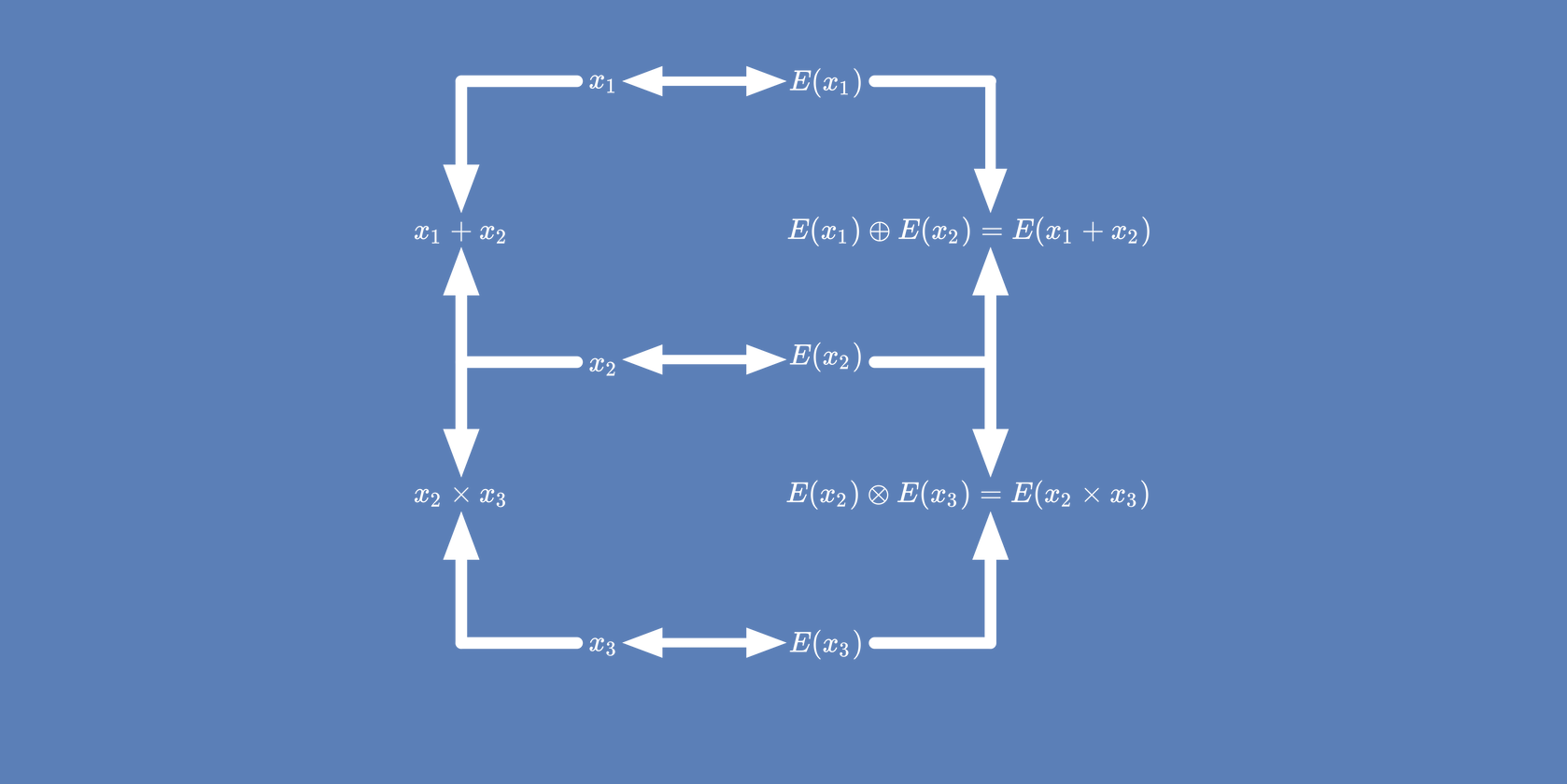 |
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic Encryption
is a form of encryption that allows computations to be performed
on encrypted data without decrypting it. Homomorphic
encryption is used for privacy-preserving outsourced storage and
computation. This allows data to be encrypted and out-sourced to
commercial cloud environments for processing,
while remain encrypted.
→
continue
|
 |
Machine Learning
Machine Learning
is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the
development and study of algorithms that can learn from data and
generalize, and thus perform tasks without explicit instructions.
Machine learning approaches have been applied to many fields
including large language models, computer vision, speech
recognition, agriculture, and medicine.
→
continue
|